State of Charge meter using a Teensy 4.0
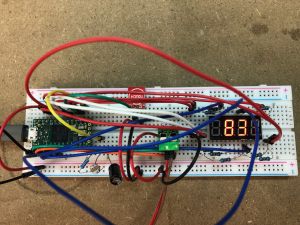
This is a CAN bus state-of-charge meter based on a Teensy 4.0. Teensy's aren't the cheapest boards (an STM32 is a tenth of the price), but they are tiny, have on-board CAN and are very easy to develop for.
It displays a state-of-charge or voltage value according the integer number sent over CAN bus to the configured address(es)
SoC values between 0 and 1000 will be displayed as " 0.0" to "100 ". The display flashes " 0.0" when it reaches zero. Anything else (or no data) will be displayed as "----"
Voltage values between 1 and 999 will be displayed as " 1V" to "999V ". Anything else (or no data) will be displayed as "---V"
A touch sensor allows you to toggle the display between SoC and voltage.
It includes automatic night time dimming.
Component list
- Teensy 4.0 board
- SN65HVD230-based CAN transceiver
- 3461BS-1 4 digit common anode 7 segment display
- 8x 220R resistors
- Photocell
- 10k resistor
- 47uF capacitor
- TTP223 Capacitive Touch Switch
Wiring
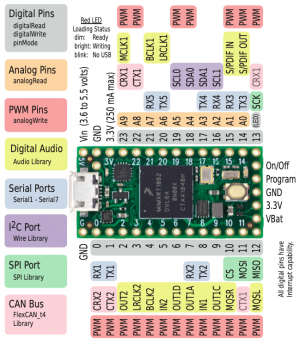
Follow the Teensy 4.0 connection schematic
- Connect the CAN transceiver to Teensy 3.3V, GND, CRX2 and CTX2
- Connect the LED D1, D2, D3 and D4 digit pins to Teensy 5, 4, 3, 2
- Connect the LED a, b, c, d, e, f, g and DP segments to Teensy 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23 via 220R resistors
- Connect the Photocell to Teensy 3.3V and A0. Connect A0 to GND via a 10k resistor and 47uF capacitor in parallel.
- Connect the Touch Switch to Teensy 3.3V, GND and 15
You'll need suitable 12V -> 5V power supply for automotive use. For development, it'll work fine off 5V USB.
Code
Fire up Teensyduino.
Install the FlexCAN_T4 library
Paste in the following code:
// CAN bus state-of-charge meter for Teensy 4.x and 4-digit 7-segment display
// Includes automatic LED brightness control
//
// Usage: send integer number over CAN bus to configured address
// SoC values between 0 and 1000 will be displayed as " 0.0" to "100 "
// The display flashes " 0.0" when it reaches zero
// Anything else (or no data) will be displayed as "----"
// Voltage values between 1 and 999 will be displayed as " 1V" to "999V "
// Anything else (or no data) will be displayed as "---V"
// Touch selection to toggle display between SoC and voltage
//
// electric_dart 2021
// define display
// values below are for 3461BS-1 4 digit common anode 7 segment display
const int ledDigits = 4; // 4 digits
const int ledSegments = 7; // 7 segments
const int pinSegment[ledSegments] = {16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22}; // pins for a,b,c,d,e,f,g segments
const int pinDecimalPoint = 23; // pin for decimal point
const int pinDigit[ledDigits] = {5, 4, 3, 2}; // common digit pins, left to right
const boolean ledIsCommonAnode = 1; // 1=common anode 0=common cathode
const int ledRefreshHz = 100; // minimum 50Hz to avoid flicker
const int ledFlashHz = 2; // for flashing display
// define display characters
const int zero[ledSegments] = {HIGH, HIGH, HIGH, HIGH, HIGH, HIGH, LOW};
const int one[ledSegments] = {LOW, HIGH, HIGH, LOW, LOW, LOW, LOW};
const int two[ledSegments] = {HIGH, HIGH, LOW, HIGH, HIGH, LOW, HIGH};
const int three[ledSegments] = {HIGH, HIGH, HIGH, HIGH, LOW, LOW, HIGH};
const int four[ledSegments] = {LOW, HIGH, HIGH, LOW, LOW, HIGH, HIGH};
const int five[ledSegments] = {HIGH, LOW, HIGH, HIGH, LOW, HIGH, HIGH};
const int six[ledSegments] = {HIGH, LOW, HIGH, HIGH, HIGH, HIGH, HIGH};
const int seven[ledSegments] = {HIGH, HIGH, HIGH, LOW, LOW, LOW, LOW};
const int eight[ledSegments] = {HIGH, HIGH, HIGH, HIGH, HIGH, HIGH, HIGH};
const int nine[ledSegments] = {HIGH, HIGH, HIGH, LOW, LOW, HIGH, HIGH};
const int blank[ledSegments] = {LOW, LOW, LOW, LOW, LOW, LOW, LOW};
const int dash[ledSegments] = {LOW, LOW, LOW, LOW, LOW, LOW, HIGH};
const int volt[ledSegments] = {LOW, LOW, HIGH, HIGH, HIGH, LOW, LOW};
// add additional characters here if required
const int* character[13] = {zero, one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, nine, blank, dash, volt};
// photocell parameters
int pinPhotocell = 14; // photocell pin
int photocellDark = 500; // adjust dark level for your photocell
int photocellLight = 1000; // adjust light level for your photocell
// touch parameters
int pinOnboardLED = 13;
int pinTouch = 15;
int touchCurrentState;
int touchLastState;
// CAN bus setup
const long canIDsoc = 0x350; // set this to match your SoC CAN bus ID
const long canIDvoltage = 0x522; // set this to match your voltage CAN bus ID
const long canSpeed = 500000; // set this to match your CAN bus speed
const long canTimeout = 10; // seconds to wait without data before showing error
#include <FlexCAN_T4.h>
FlexCAN_T4<CAN2, RX_SIZE_256, TX_SIZE_16> Can0; // Using CAN2 on pins 0 & 1
// internal variables
int ledRefreshMilliseconds = 1000 / (ledDigits * ledRefreshHz); // milliseconds
int ledOnMicroseconds; // microseconds
unsigned long nowMilliseconds;
unsigned long nowMicroseconds;
unsigned long nextRefreshMilliseconds = 0;
unsigned long nextBlankMicroseconds = 0;
unsigned long nextTimeoutMilliseconds = 0;
unsigned long nextFlashMilliseconds = 0;
boolean ledFlashState = 1;
int digitSelect = 0;
int readingSoC = -1;
int readingVoltage = -1;
int photocellReading;
int ledBrightness; // score 1 to 10
int displayMode = 0; // 0=SoC, 1=Voltage
void clearDisplay()
{
for (int i = 0; i < ledDigits; ++i)
{
digitalWrite(pinDigit[i], HIGH ^ ledIsCommonAnode);
}
}
void writeDisplayDigit(int digit, int value, boolean decimal)
// digit: numbered left-to-right, beginning at zero
// value: the character to display from character[] array
// decimal: set this to 1 to switch the decimal point on
{
for (int i = 0; i < ledSegments; ++i)
{
digitalWrite(pinSegment[i], character[value][i] ^ ledIsCommonAnode);
}
digitalWrite(pinDecimalPoint, decimal ^ ledIsCommonAnode);
digitalWrite(pinDigit[digit], LOW ^ ledIsCommonAnode);
}
void writeDisplaySoC(int digit, int value) // customise this section according to what you want to display
{
if (value == 1000) { // display "100 " if the input value is 1000
switch (digit) {
case 0:
writeDisplayDigit(0, 1, 0);
break;
case 1:
writeDisplayDigit(1, 0, 0);
break;
case 2:
writeDisplayDigit(2, 0, 0);
break;
}
}
else if (value >= 100 and value < 1000) { // display " 99 " to " 10 " for input values from 999 to 100
switch (digit) {
case 1:
writeDisplayDigit(1, value / 100, 0);
break;
case 2:
writeDisplayDigit(2, (value / 10) % 10, 0);
break;
}
}
else if (value >= 1 and value < 100) { // display " 9.9" to " 0.1" for input values from 99 to 1
switch (digit) {
case 2:
writeDisplayDigit(2, value / 10, 1);
break;
case 3:
writeDisplayDigit(3, value % 10, 0);
break;
}
}
else if (value == 0) { // display flashing " 0.0" for input value 0
if (nowMilliseconds > nextFlashMilliseconds) {
nextFlashMilliseconds = nowMilliseconds + ( 1000 / ledFlashHz );
ledFlashState = ledFlashState ^ 1;
}
if (ledFlashState == 1) {
switch (digit) {
case 2:
writeDisplayDigit(2, 0, 1);
break;
case 3:
writeDisplayDigit(3, 0, 0);
break;
}
}
else {
switch (digit) {
case 2:
writeDisplayDigit(2, 10, 1);
break;
case 3:
writeDisplayDigit(3, 10, 0);
break;
}
}
}
else { // display "----" for anything else
writeDisplayDigit(digit, 11, 0);
}
}
void writeDisplayVoltage(int digit, int value) // customise this section according to what you want to display
{
if (value >= 100 and value < 1000) { // display "100V" to "999V" for input values 100 to 999
switch (digit) {
case 0:
writeDisplayDigit(0, (value / 100) % 10, 0);
break;
case 1:
writeDisplayDigit(1, (value / 10) % 10, 0);
break;
case 2:
writeDisplayDigit(2, value % 10 , 0);
break;
case 3:
writeDisplayDigit(3, 12, 0);
break;
}
}
else if (value >= 10 and value < 100) { // display " 10V" to " 99V " for input values from 10 to 99
switch (digit) {
case 1:
writeDisplayDigit(1, value / 10, 0);
break;
case 2:
writeDisplayDigit(2, value % 10, 0);
break;
case 3:
writeDisplayDigit(3, 12, 0);
break;
}
}
else if (value >= 1 and value < 10) { // display " 1V" to " 9V " for input values from 1 to 9
switch (digit) {
case 2:
writeDisplayDigit(2, value % 10, 0);
break;
case 3:
writeDisplayDigit(3, 12, 0);
break;
}
}
else { // display "---V" for anything else
switch (digit) {
case 0:
writeDisplayDigit(0, 11, 0);
break;
case 1:
writeDisplayDigit(1, 11, 0);
break;
case 2:
writeDisplayDigit(2, 11, 0);
break;
case 3:
writeDisplayDigit(3, 12, 0);
break;
}
}
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); //initialise serial communications at 9600 bps
// Initialise CAN bus
delay(1000); // allow CAN hardware to stabilise
Can0.begin();
Can0.setBaudRate(canSpeed);
Can0.setMaxMB(16);
Can0.enableFIFO();
Can0.enableFIFOInterrupt();
Can0.onReceive(canDataReceived);
Can0.mailboxStatus();
// Initialise LED display
// segement pins
for (int i = 0; i < ledSegments; ++i)
{
pinMode(pinSegment[i], OUTPUT);
}
// decimal point pin
pinMode(pinDecimalPoint, OUTPUT);
// digit pins
for (int i = 0; i < ledDigits; ++i)
{
pinMode(pinDigit[i], OUTPUT);
}
clearDisplay();
pinMode(pinOnboardLED, OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinPhotocell, INPUT);
pinMode(pinTouch, INPUT);
touchCurrentState = digitalRead(pinTouch);
}
void canDataReceived(const CAN_message_t &msg) {
// Serial.print("MB "); Serial.print(msg.mb);
// Serial.print(" OVERRUN: "); Serial.print(msg.flags.overrun);
// Serial.print(" LEN: "); Serial.print(msg.len);
// Serial.print(" EXT: "); Serial.print(msg.flags.extended);
// Serial.print(" TS: "); Serial.print(msg.timestamp);
// Serial.print(" ID: "); Serial.print(msg.id, HEX);
// Serial.print(" Buffer: ");
// for ( uint8_t i = 0; i < msg.len; i++ ) {
// Serial.print(msg.buf[i], HEX); Serial.print(" ");
// } Serial.println();
switch (displayMode) { // according to display mode
case 1:
if (msg.id == canIDvoltage) {
// Matching voltage CAN bus frame arrived!
//readingVoltage = (msg.buf[2] << 24) | (msg.buf[3] << 16) | (msg.buf[4] << 8) | (msg.buf[5]); // now piece it together
readingVoltage = (msg.buf[6] << 8) | (msg.buf[7]); // now piece it together
nextTimeoutMilliseconds = nowMilliseconds + (canTimeout * 1000); // set next timeout
}
break;
default:
if (msg.id == canIDsoc) {
// Matching SoC CAN bus frame arrived!
readingSoC = (msg.buf[6] << 8) | (msg.buf[7]); // now piece it together
nextTimeoutMilliseconds = nowMilliseconds + (canTimeout * 1000); // set next timeout
}
break;
}
}
void loop() {
// add extra code here
// pot input for testing without CAN bus
//reading = analogRead(pin_pot);
//reading = map(reading, 10, 1023, 0, 1000);
touchLastState = touchCurrentState;
touchCurrentState = digitalRead(pinTouch);
if(touchLastState == LOW && touchCurrentState == HIGH) {
// toggle display
displayMode = !displayMode;
// control LED arccoding to the toggled state
digitalWrite(pinOnboardLED, displayMode);
}
//
//
Can0.events();
// take a timestamp
nowMilliseconds = millis();
nowMicroseconds = micros();
// calculate required LED brightness score (1-10) and set time to remain on (in microseconds) as a proportion of the refresh interval
photocellReading = analogRead(pinPhotocell);
photocellReading = constrain(photocellReading, photocellDark, photocellLight);
ledBrightness = map(photocellReading, photocellDark, photocellLight, 1, 10);
ledOnMicroseconds = ledBrightness * ledRefreshMilliseconds * 100; // microseconds
// timeout if no data received
if (nowMilliseconds > nextTimeoutMilliseconds) {
readingSoC = -1; // display "----"
readingVoltage = -1; // display "----"
}
// is it time to refresh display?
if (nowMilliseconds > nextRefreshMilliseconds) {
nextRefreshMilliseconds = nowMilliseconds + ledRefreshMilliseconds; // set the time in milliseconds for the next refresh
nextBlankMicroseconds = nowMicroseconds + ledOnMicroseconds; // set the time in microseconds for LEDs to remain on (for dimming)
// multiplexed display, so enable one digit at at time
switch (displayMode) { // according to display mode
case 1:
writeDisplayVoltage(digitSelect, readingVoltage);
break;
default:
writeDisplaySoC(digitSelect, readingSoC);
break;
}
++digitSelect; // we'll do the next digit on the next pass
if (digitSelect > ledDigits - 1 ) { // all digits done?
digitSelect = 0; // wrap around to first digit again.
}
}
// is it time to switch the LEDs off?
if (nowMicroseconds > nextBlankMicroseconds ) {
clearDisplay();
}
}
Try it out!
Compile and upload the code to your Teensy board. The code isn't very complicated, so I set mine to run at 150MHz.
If you send CAN data to the specified node ID, the display should spring into life.
<YouTube></nowiki>https://youtu.be/s-Gadj3Rnxw<nowiki></youtube>