Nissan Leaf Motors
The Nissan EM motor is an electrical motor series manufactured by Nissan Motors. It is used in a variety of vehicles, mainly the Nissan Leaf. They are 3-phase AC synchronous power electric motors, utilizing interior neodymium permanent magnets.
Significant Community Projects
Openinverter development on the Nissan Leaf platform is fairly mature. The Openinverter forum section dedicated to Nissan components is here. While the Leaf has only 2 official generations (as of 2023), the forums tend to refer to ‘gen1’, gen2’ and ‘gen3’ packages.
The official 1st generation Leaf (2010-2017) included two different motor packages, which the forum refers to as gen1 and gen2. Gen1 refers to the EM61 package. Gen2 refers to the early EM57 package.
The forum uses Gen3 to refer to the late EM57 package[1], found in the official 2nd generation Leaf (2018+). The EM57 packages are visually identical, but gen2 has a silver upper case and gen3 has a black upper case.
The EM47 platform (used in \Nissan's e-POWER lineup, which is a series hybrid platform) has received very little development as of early 2023.
There have been a number of open source community projects based on the Nissan Leaf. These are listed, with links and proper attribution, in this section.
- BRAT INDUSTRIES has motor couplers and adapter plates available here https://bratindustries.net/ and has opensourced an adapter plate for the EM57 motor, which can be found here.
- Open inverter replacement board for gen2 inverter: Nissan Leaf Gen2 Board.
- ZombieVerter VCU can bus controller: ZombieVerter VCU.
EM61
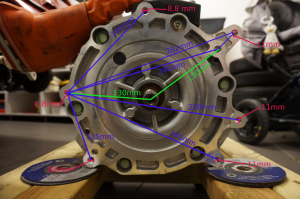
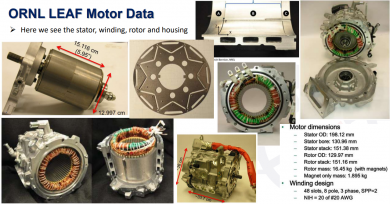
The EM61 made its debut in 2010. It was used only in the first generation Nissan Leaf (ZE0 2010-2012). It is a stand alone IPMSM motor, with a theoretical peak power output of a 250kw+.
Regarded as Nissan’s ‘R&D’ motor, due to the presence of stronger rare earth magnets. This results in a slightly higher torque output efficiency than the second generation EM57 motor.
In the stock OEM leaf, the motor was battery and inverter limited to 80kw and made 280Nm of peak torque.
Weight without gearbox or (separate) inverter: 56 kg.[2]
Final drive ratio: 7.937:1.[3]
EM57

The EM57 is an improvement over the first generation. It was first released with the AZE0 Nissan Leaf refresh in 2013.
This motor features a smaller footprint, allowing for 11.7 kg of weight savings in the inverter/motor package. The motor also trades some peak torque for a more efficient power range.
This link leads to maintenance document for resolver wiring:
https://openinverter.org/forum/viewtopic.php?p=47467#p47467
The EM57 utilizes a stacking architecture for the power electronics, compared to the isolated nature of the EM61 motor. Whereas the inverter and motor of the EM61 were separate units connected by cables, the EM57 is an integrated package that is bolted together.
Nissan has continued to use the EM57 motor through multiple generation of vehicles, resulting in mechanically plug and play OEM inverter upgrades.
Inverters currently compatible with the EM57 motor:
- gen 2 leaf 80kw inverter
- gen 3 leaf 110kw inverter
- gen 3 leaf 160kw inverter
It is used in the following electric vehicles:
- Nissan Leaf (AZE0 2013-2017)
- Nissan e-NV200 (2014-Present)
- Nissan Leaf (ZE1 40kWh, 2018-Present)
- Nissan Leaf (ZE1 62kWh, 2019-Present)
It is also used in the following hybrids:
- Nissan Note e-Power (2017-Present)
- Nissan Serena e-Power (2018-Present)
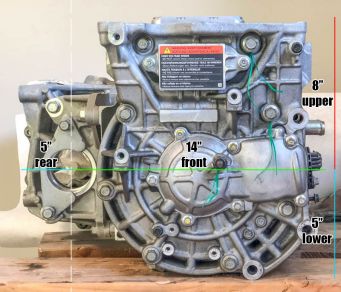
EM57 Dimensions
The below photographs show the rough dimensions of the EM57. These photos were taken from https://www.diyelectriccar.com/threads/nissan-leaf-cad-files.203894/#post-1064439, which has more detailed information.

EM57 Plugs and connectors
The resolver plug is Yazaki 7283-8855-30 (https://www.auto-click.co.uk/7283-8855-30?search=7283-8855-30)

EM47
The EM47 motor released in 2020 with the refreshed Nissan Note. It is only used in Nissan's e-POWER lineup, which is a series hybrid platform. It features a 40% size reduction and 30% weight reduction
It is used in the following hybrids:
- Nissan Note e-Power (2020-Present)
MM48
The MM48 engine is found in 4WD variant of their e-power Hybrid system, powering the read axle. It also used as a main engine (part number 290A07PA0A) in Nissan Sakura, currently marketed for Japan only. The parameters, per Wikipedia, are: 50 kW (67 hp; 68 PS) @ 4775–10,024 rpm, 100 N⋅m (10.2 kg⋅m; 73.8 lb⋅ft) @ 0–4775 rpm. Speed reducer gear ratio 7.282:1[4] (2021 Nissan Aura).
This newly developed Meidensha e-Axle is used in the drive motors of Nissan's Note, Aura e-4WD rear, and Sakura EVs. The e-Axle for e-4WD rear and Kei-class (mini-vehicle) EVs is compact and consists of an inverter with direct-cooled IGBTs, an IPMSM-type motor with SC windings, and a speed reducer. Although the housing shape and other features have been adapted to the mounting requirements of the Aura e-4WD rear, the basic parts such as the motor's active parts (electromagnetic circuit) are believed to be the same as those of same model (MM48) of both the e-4WD rear and Kei-class EV drive motor.[5]

Output Splines
Couplers for the output shaft can be purchased from https://bratindustries.net/. It's also been found that a drive shaft holding tool matches the splines, a Solas WR014H, https://openinverter.org/forum/viewtopic.php?p=79794#p79794
See also
Citations
- ↑ https://openinverter.org/forum/viewtopic.php?p=15702#p15702
- ↑ https://www.energy.gov/sites/prod/files/2014/03/f13/ape006_burress_2013_o.pdf
- ↑ https://nissanleafforum.com/download/2011_LEAF_Specs.pdf
- ↑ https://history.nissan.co.jp/ARCHIVES/PDF/AURA/E13/20211224/aura_specsheet.pdf
- ↑ https://www.marklines.com/en/report/rep2381_202210